EXPLORE
Got a Question? Connect with our experts.
Talk to an Expert
Got a Question? Connect with our experts.
Talk to an Expert
When launching a new product, the goal is to validate your idea with minimal resources. This is where the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) concept comes in.
An MVP is a scaled-down version of your product that contains just enough features to solve the core problem for your users.
The primary purpose of an MVP is to test assumptions, collect feedback, and determine whether the product can scale.
A vital component of this process is measuring and tracking the success of your MVP through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
KPIs are the metrics that provide a clear indication of whether your MVP is heading in the right direction.
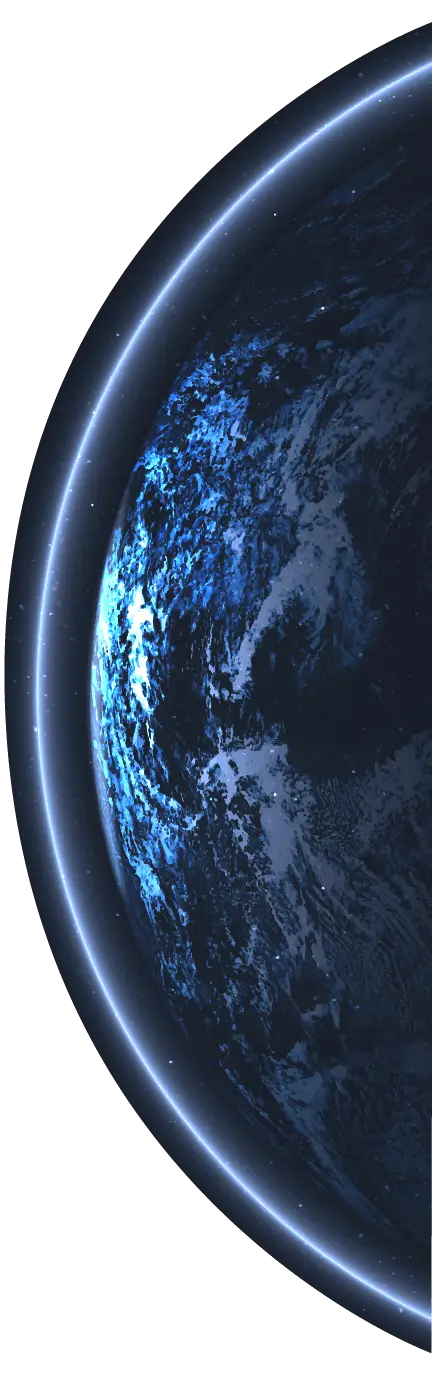
Define Your MVP's Objectives: Before defining KPI
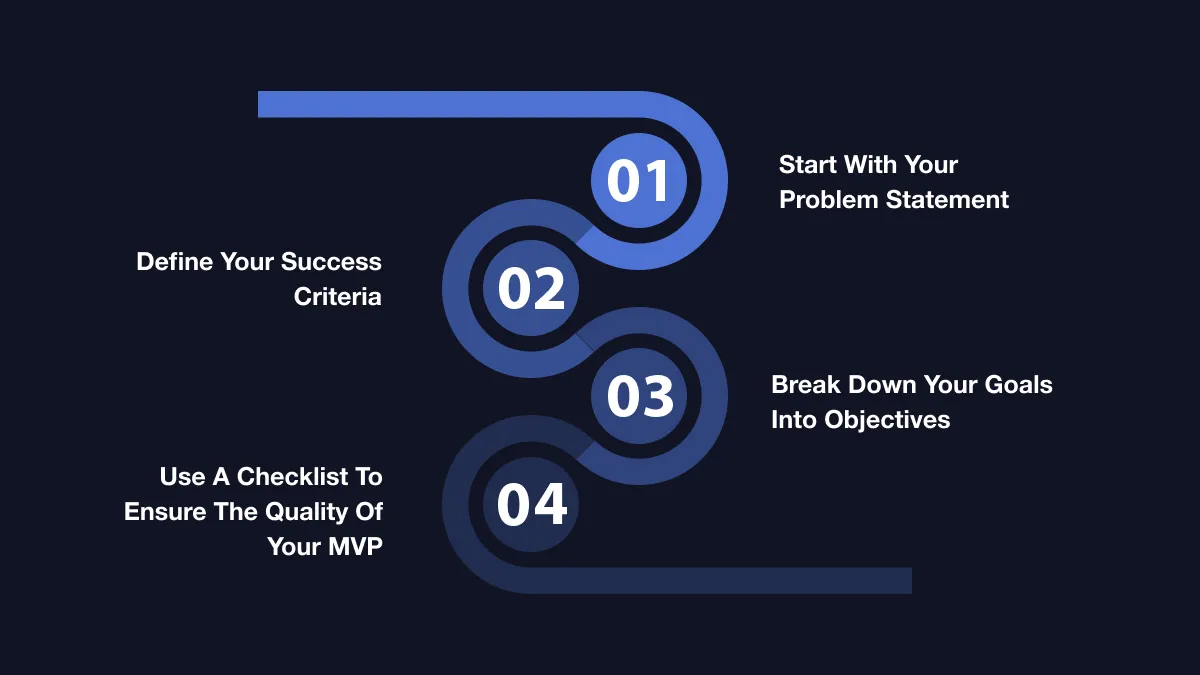
Before you start measuring anything, it is crucial to clearly understand your MVP’s objectives.
These objectives will drive the selection of KPIs, ensuring that you track what truly matters for your product's success.
What are MVP Objectives?
MVP objectives are the core goals you want to achieve with your product in its initial version. They should align with your long-term product vision but be narrowly focused to validate the most critical aspects of the product.
An MVP’s objective could look like either of the following:
- Validating the core value proposition - Do users see the value in what you are offering?
- Testing the market demand - Is there a sizable audience willing to pay for or use your product?
- Gathering feedback for iteration - Do you need insights to refine features or solve user pain points?
Real-life Example Of MVP Objectives
Back in 2009, Amazon acquired the online retail company Zappos. Back then, Zappos was just an MVP, its objective was simply to validate the idea that people would buy shoes online.
Their MVP was a simple website with images of shoes from local stores.
The main goal was to test if customers were willing to make an online purchase, even though Zappos did not have the inventory at the time.
Clear objectives are critical because they determine which KPIs will effectively measure success. Without them, you risk tracking irrelevant data.
Understand KPIs for MVP: Why Do They Matter?

Before we dive into specific KPIs, it is essential to understand their role in the MVP process.
KPIs are the metrics that help you understand whether your MVP is meeting its goals.
They give you insights into user behavior, engagement, retention, and how well your product is addressing customer pain points.
Why are KPIs Important for MVP?
KPIs allow you to test assumptions early and validate your product’s potential before committing large resources to development. They help you make data-driven decisions.
For instance, if user retention is low, you can prioritize improving that aspect of the product.
By continuously tracking KPIs, you can measure the growth of your MVP, track how well you are acquiring users, and identify potential issues before they become major problems.
MVP KPIs Example
When Dropbox first launched its MVP in the form of an explainer video, one of the key KPIs was the sign-up rate.
They tracked how many viewers signed up for the product after watching the video.
This simple KPI provided early feedback about whether there was market demand for their product idea, helping them decide whether to proceed with building the full product.
KPIs help you understand if your MVP is worth scaling and where to focus your efforts.
Types of KPIs to Measure Your MVP
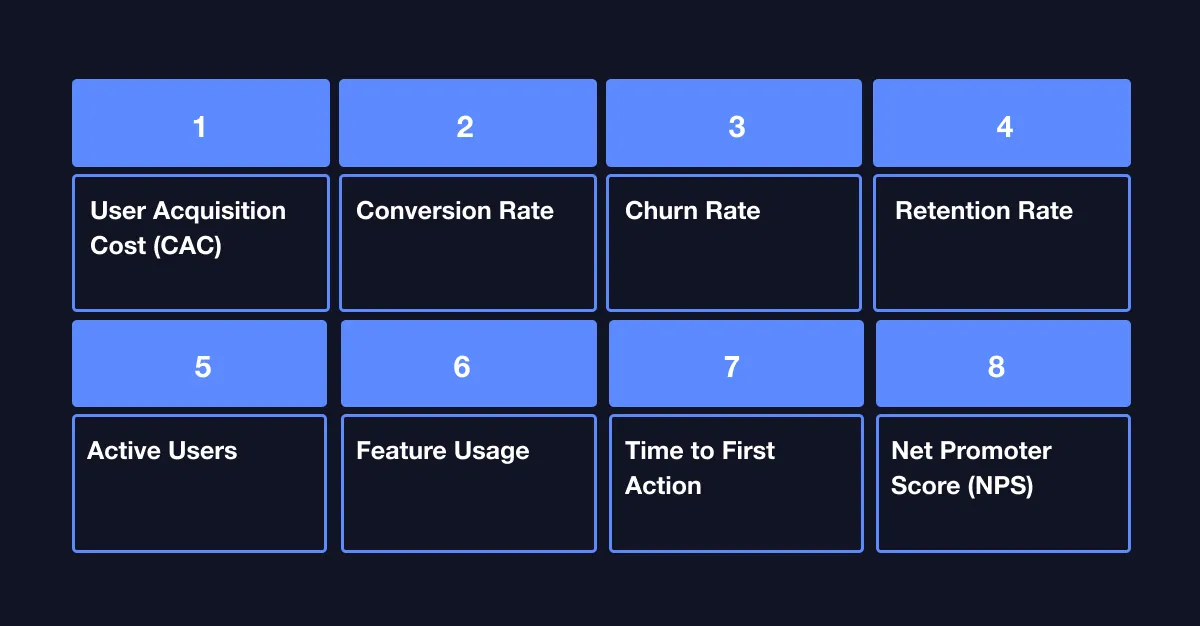
KPIs for MVPs vary depending on the type of product, stage of development, and specific goals.
However, some KPIs are universally valuable, regardless of the MVP type.
The following are the core KPIs for any MVP
User Acquisition Cost (CAC)
User Acquisition Cost (CAC) represents the cost of acquiring a new customer and is crucial in understanding the efficiency of your marketing and acquisition strategies.
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is a percentage of users who take the desired action (e.g., sign-up, purchase, etc.). This tells you whether your product’s value proposition is compelling enough to drive action.
Churn Rate
The churn rate is a percentage of users who stop using your product. A high churn rate signals that your MVP is not providing enough value to retain users.
Retention Rate
The retention rate is the percentage of users who continue to engage with your product after the first use. Retention is often more important than acquisition for determining long-term success.
Active Users
Active users include Daily Active Users (DAU) and Monthly Active Users (MAU). These metrics tell you how many users are actively engaging with your product over a given time period.
Feature Usage
The feature usage metric tracks how often specific features of your MVP are used, helping you prioritize which features to improve or expand.
Time to First Action
Time to First Action is the time it takes for a user to complete the first key action after signing up. Shorter times typically indicate a smoother user experience.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The net promoter score indicates how likely users are to recommend your MVP to others, which is a strong signal of satisfaction.
Instagram's MVP KPIs Example
For Instagram, the MVP involved simple photo sharing with a basic filter.
The core KPIs they focused on were user acquisition (sign-ups) and engagement (posts shared, photos liked). These early KPIs validated that people enjoyed sharing photos and interacting with the app.
Define and track the KPIs that directly align with your MVP goals, focusing on user engagement, retention, and the initial signs of product-market fit.
What are Success Metrics in MVP?

Success metrics are the indicators that will tell you when your MVP has achieved product-market fit.
Product-market fit is a step in which you test your MVP to ensure that it truly addresses a real market need.
Instead of building a product in a vacuum, you confirm that what you are creating solves a problem that people are willing to pay for.
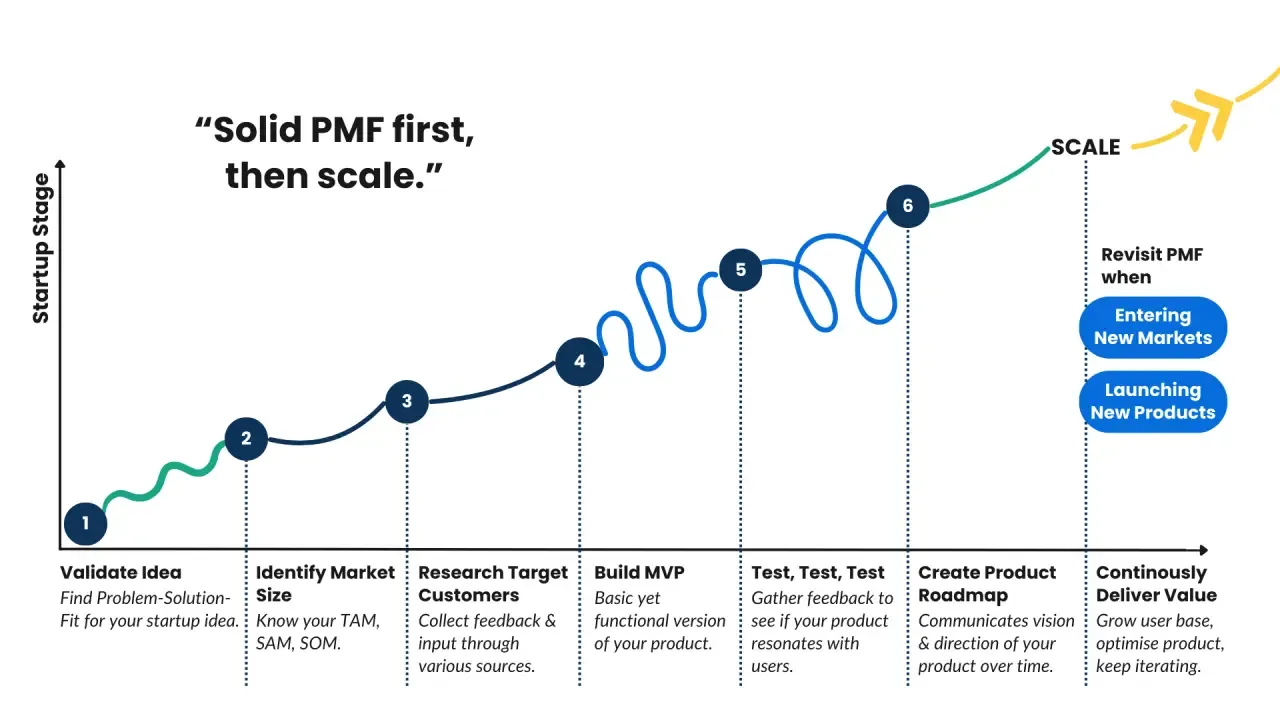
Source: MarketSizer
Success metrics are different from KPIs in that they provide a benchmark for long-term success and help evaluate overall product growth.
Examples of MVP Success Metrics:
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) measures the total revenue you expect from a customer over their entire relationship with your product. For an MVP, a positive CLV-to-CAC ratio means you're acquiring customers profitably.
CLV is typically calculated using the following formula:
CLV = Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) x Average Customer Lifespan (in months or years)
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
If you’re building a subscription-based MVP, Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is an excellent measure of the sustainability of your product and market demand. It can tell you whether there is consistent demand and if users are willing to pay for the service.
The formula for MRR depends on the type of subscription model you have, but a simple approach is:
MRR = ∑ (Monthly Subscription Fee x Number of Active Subscribers)
Number of Paying Users
This is the total count of users who have made a payment, whether it is a one-time purchase or a subscription.
This metric indicates if your MVP is providing enough value to prompt users to make financial commitments.
Monitor the number of users who complete a purchase or sign up for a paid plan, depending on your business model.
Monthly ARPU (Average Revenue Per User)
It is the average revenue you earn from each active user in a given month.
ARPU helps you understand how much revenue you can expect from each user. It is particularly useful for subscription models as it shows the monetization efficiency of your product.
ARPU = Total Monthly Revenue / Total Active Users
User Ratings and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
User ratings (often out of 5 stars) and the CSAT score measure how satisfied customers are with your MVP. CSAT is often collected through post-interaction surveys asking users to rate their experience on a scale of 1-10 or 1-5.
Positive ratings and high CSAT scores indicate that your MVP is meeting user needs and expectations. This is crucial for building user retention and creating positive word-of-mouth.
CSAT = (Number of Satisfied Users / Total Survey Responses) x 100
A CSAT score of 80% or higher is often seen as good.
Download Rate
The download rate refers to how often your app or product is being downloaded in a given time period. For mobile apps, this metric is important to track initial interest.
A high download rate indicates interest and demand for your MVP, while a low rate suggests that you may need to improve your marketing, product appeal, or visibility.
This is typically tracked through app stores (Google Play, Apple App Store) or other distribution platforms like your website.
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the profitability of your MVP relative to the resources you have invested in developing and launching it.
This is a key metric for understanding if the resources and efforts spent on your MVP are yielding profitable results.
ROI = (Net Profit / Total Investment) x 100
One of the clearest success metrics is whether your MVP has achieved Product Market Fit (PMF), often measured by retention rates, customer satisfaction, and NPS scores.
Airbnb's MVP KPIs Example
Airbnb’s MVP success metrics included metrics like repeat bookings and host sign-ups. Their success was determined when they saw a high rate of host retention and a growing number of repeat users, indicating that the platform had found market fit.
Success metrics indicate if your MVP is ready to move beyond its early testing phase. These metrics also help you understand if you are on track for scaling the product.
KPIs for SaaS MVPs
If you are building an SaaS MVP, the KPIs you choose will differ somewhat from other MVP types.
The goal with a SaaS MVP is often to establish a solid base of recurring revenue and ensure user engagement.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) tracks subscription revenue on a monthly basis, showing whether the SaaS MVP is gaining traction and converting free users into paying customers.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) helps in understanding how much it costs to acquire each customer and can help ensure your SaaS MVP’s growth is sustainable.
For SaaS MVPs, minimizing churn is crucial. A low churn rate shows that users find value in the product and are sticking around.
User Engagement Metrics include metrics like feature adoption, time spent in the app, and DAU/MAU. These metrics help ensure that users are not just signing up but actively using the product.
Slack's MVP KPIs Example
At the beginning, Slack focused on tracking key engagement metrics such as daily active users (DAU) and messages sent per user. By tracking these KPIs, Slack was able to understand how users interacted with the product and ensure their MVP was on track to scale.
For SaaS MVPs, focus on measuring MRR, churn rate, user engagement, and customer acquisition costs to track growth and refine your product.
Iterating and Refining Based on KPIs
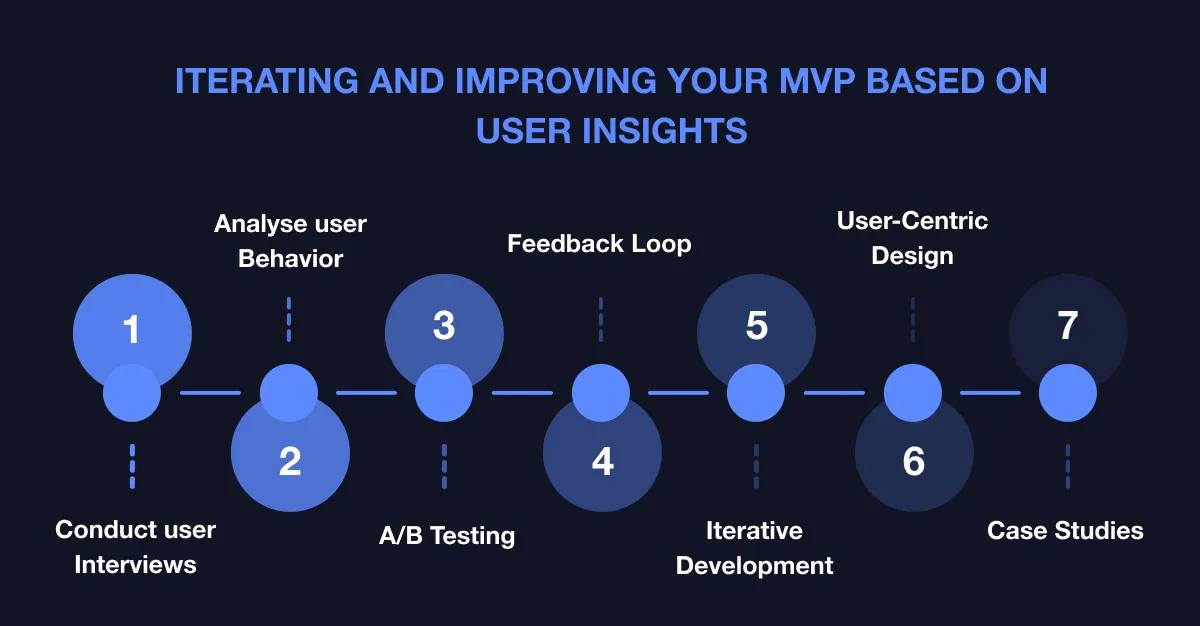
One of the main reasons for building an MVP is to validate ideas and gather feedback to improve the product. Once you have your KPIs in place, they will provide insights that guide your iteration process.
How to Use KPIs for Iteration?
Pivot or Persevere
If KPIs like churn rate are high, it could indicate that the product is not solving a big enough problem.
On the other hand, high user retention and referral rates can signal that your MVP is on the right track and should be expanded.
A/B Testing
Regularly conduct A/B tests on different features or flows to see what drives better results. For example, different onboarding experiences can be tested, and their effects on conversion rates can be measured.
Customer Feedback
Use feedback from surveys or interviews to understand the “why” behind the data. If users are dropping off at a specific point in the user journey, investigate further to improve the experience.
Spotify's MVP KPIs Example
Spotify tested its MVP with a limited feature set to track user engagement and session length. They found that users were engaging with the platform more when they could easily create playlists. Based on this KPI, they iterated on the feature and expanded it, which drove more engagement.
Use KPIs to make informed decisions about when to pivot or iterate. Regular tracking ensures that you are making adjustments based on actual user behavior, not assumptions.
Set Up Your MVP's Tracking Tools
Once your KPIs and success metrics are defined, it is essential to choose the right tools to track them. Without proper tracking, you will be flying blind when it comes to measuring success.
Tracking Tools for MVPs:
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the best for tracking general website traffic, conversion rates, and user engagement on landing pages.
Mixpanel
Mixpanel provides detailed user tracking, cohort analysis, and feature usage data, making it great for MVPs focused on understanding user behavior.
Amplitude
Amplitude is Similar to Mixpanel but offers a more comprehensive look at user journeys, helping you understand how people move through your product.
Hotjar
Hotjar is a tool for tracking user behavior with heatmaps, session recordings, and surveys. Perfect for gauging user engagement and satisfaction.
Spotify's Tracking Tools Example
Spotify used Mixpanel early on to track user behavior and gather insights into how users interacted with their MVP, such as what music genres they listened to the most. This helped refine the product and improve its core offering.
Choose the tools that align with the KPIs you are tracking. Proper data tracking will ensure that you can make informed decisions about your MVP.
Effective Communication of KPIs
Once KPIs are set and tracked, the next step is communicating the results. This is key for ensuring alignment across teams and stakeholders.
Use tools like Google Looker Studio, Tableau, or Klipfolio to create custom dashboards that update in real time, making it easier for your team to monitor KPIs. Also, schedule weekly or monthly reports to track progress, discuss insights, and refine strategies.
Zynga Effective Collaboration Example
Zynga, a gaming company, uses real-time dashboards to track user engagement metrics like session length, in-app purchases, and user retention. The dashboards help decision-makers act quickly and adjust product strategies to boost user retention.
Make your KPIs easily accessible to stakeholders through dashboards or regular reports. Transparency in KPI tracking ensures all teams are aligned with product goals.
Monitor Your MVPs' Data
source: jumpstartthemes.com
Tracking your MVP’s KPIs is not enough. You need to actively monitor and analyze the data to make informed decisions and refine the product.
Automated reporting so you can receive real-time insights into your KPIs. This ensures you stay on top of any fluctuations in user behavior. Tools like Google Looker Studio or Tableau can help you create custom dashboards for quick insights into your KPIs.
Conduct regular A/B tests to see how changes affect user behavior. For instance, you might test different onboarding processes and compare which leads to better conversion rates.
Regular monitoring of your MVPs’ KPIs helps you make real-time improvements. Use the data to guide your next steps, whether it is refining features or testing new ones.
Best Practices for Tracking MVP KPIs
Tracking the right KPIs for your MVP is essential, but how you track them matters, too.
Here are some best practices to ensure your KPI tracking is efficient and actionable:
Invest in analytics tools that align with your product goals. Tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Amplitude help track user behavior and provide insights into which features drive the most engagement.
Each KPI should have a specific target or benchmark. For example, if you are aiming for a 5% conversion rate, you know exactly what you are working toward.
Continuously monitor your KPIs and hold regular review meetings to ensure that everyone on your team is aligned with the product goals.
While KPIs give you hard numbers, user feedback adds context. For instance, if churn is high, user interviews can reveal whether users are leaving because of product limitations or market conditions.
Conclusion
Measuring and tracking KPIs for your MVP is a crucial part of validating and refining your product. By focusing on the right metrics, such as user acquisition, retention, feature usage, and engagement, you can ensure that your MVP is on the right path to success.
Regularly analyzing these KPIs allows you to make data-driven decisions, optimize your product, and scale effectively. Whether you are testing an SaaS MVP, an e-commerce MVP, or any other type of product, KPIs are your guiding light in the journey from idea to market-fit.




